Table Of Content
Bonds can be a valuable addition to any investment portfolio, offering stability and income. But for new investors, the world of bonds can seem complex.
This article will break down the basics of bond investing, guiding you through the different types, where to buy them, and how to navigate the process with confidence.

1. Understand Bond Types
While there are many types of bonds, for beginners- these two options are the most relevant and popular, each with its own pros and cons:
-
Government Bonds
Issued by governments to finance public projects or to manage fiscal deficits. These include:
- Treasury Bonds: Issued by the government (such as the U.S. Treasury) and considered one of the safest investments.
- Municipal Bonds: Issued by state or local governments to fund public infrastructure projects like schools, roads, or utilities.
- Savings Bonds: Non-tradable bonds issued by the government, often purchased by individuals as a long-term savings tool.
Governments bonds offer low to moderate interest rates but are highly liquid and generally considered a good option for conservative investors seeking income and capital preservation.
Pros of Government Bonds | Cons of Government Bonds |
|---|---|
Low default risk | Lower yields compared to other securities |
Stable income source | May not suit aggressive investors |
Favorable for conservative investors | Interest rate risk |
Tax advantages in some cases | Limited growth potential |
Backed by government | Less attractive during high inflation |
-
Corporate Bonds
Issued by corporations to raise capital for various purposes, such as expansion, acquisitions, or debt refinancing. Corporate bonds vary in terms of credit quality and risk:
- Investment-Grade Bonds: Issued by companies with strong credit ratings, typically considered lower risk.
- High-Yield Bonds (Junk Bonds): Issued by companies with lower credit ratings or higher risk profiles, offering higher yields to compensate for the increased risk.
Corporate bonds offer higher interest rates than government or municipal bonds but carry more credit risk depending on the financial health of the issuing company.
Pros of Corporate Bonds | Cons of Corporate Bonds |
|---|---|
Higher yields than government bonds | Higher default risk than government bonds |
Diverse range of issuers and sectors | Sensitive to company's financial health |
Potential for capital appreciation | Market fluctuations affect bond prices |
Interest rate risk can impact value | Credit ratings guide investment decisions |
2. Choose Where You Prefer To Buy Bonds
There are several ways to purchase bonds, each with its own set of characteristics and considerations. Here's an overview of the primary methods:
-
Through a Broker or Brokerage Account
Many investors buy bonds through brokerage firms. This method provides access to a wide variety of bonds, including corporate, municipal, and government bonds.
Brokerages offer the convenience of buying and selling bonds through the same platform used for other investments, although they may charge fees or commissions.
Fidelity, Charles Schwab, and E*TRADE are popular brokerage firms offering bond trading.
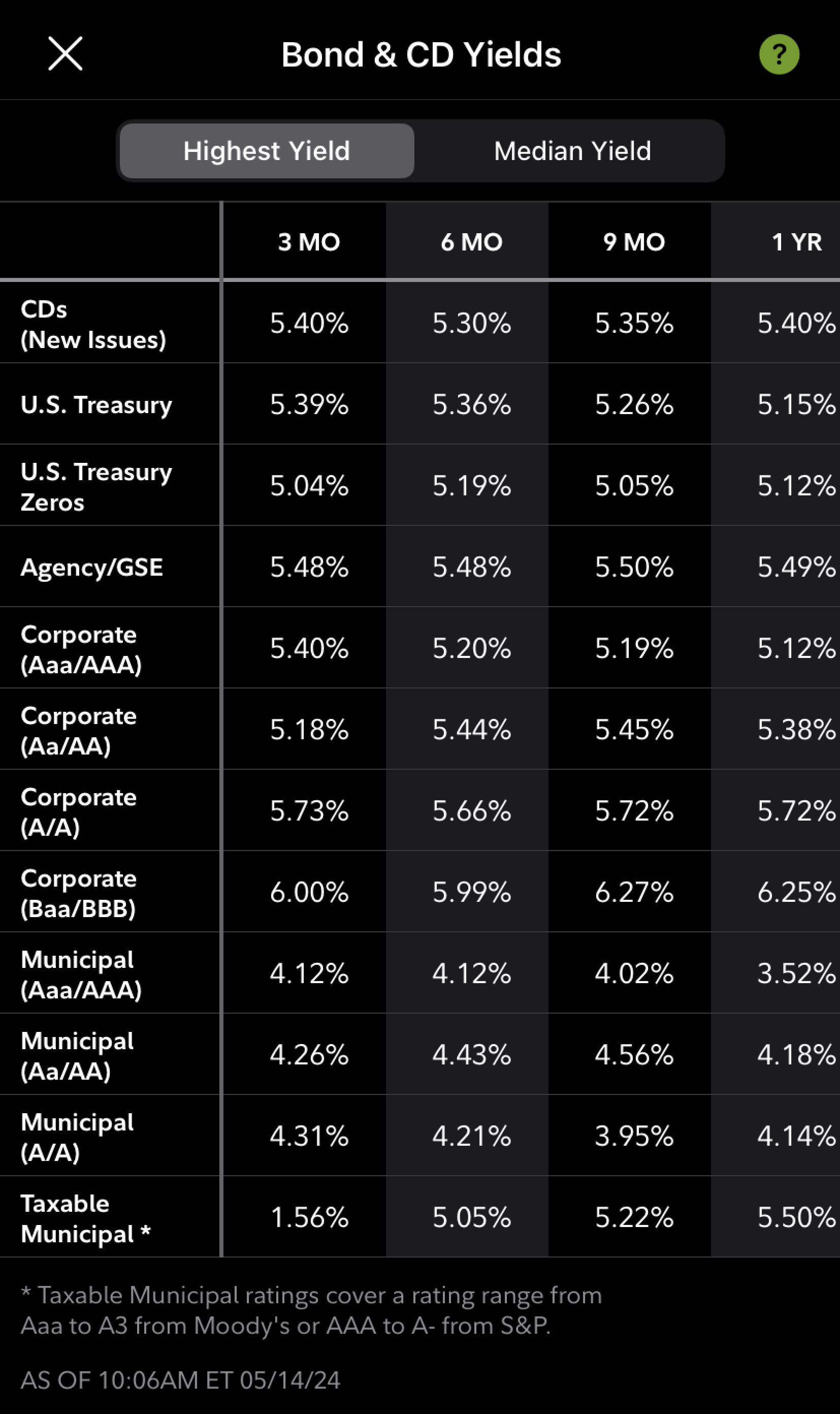
-
Directly from the Issuer at Issuance
Investors can buy bonds directly from the issuer when they are first issued. This is common with government bonds, such as U.S. Treasury bonds, which can be purchased through TreasuryDirect.gov.
-
Through a Financial Advisor or Investment Firm
Investors seeking personalized advice may opt to purchase bonds through a financial advisor or investment firm.
This approach provides professional guidance and is suited for those looking for a tailored investment strategy, though it may come with higher fees.
Firms like Merrill Lynch and Morgan Stanley provide personalized bond investment services through financial advisors.
-
You Shouldn't Buy Bonds Directly
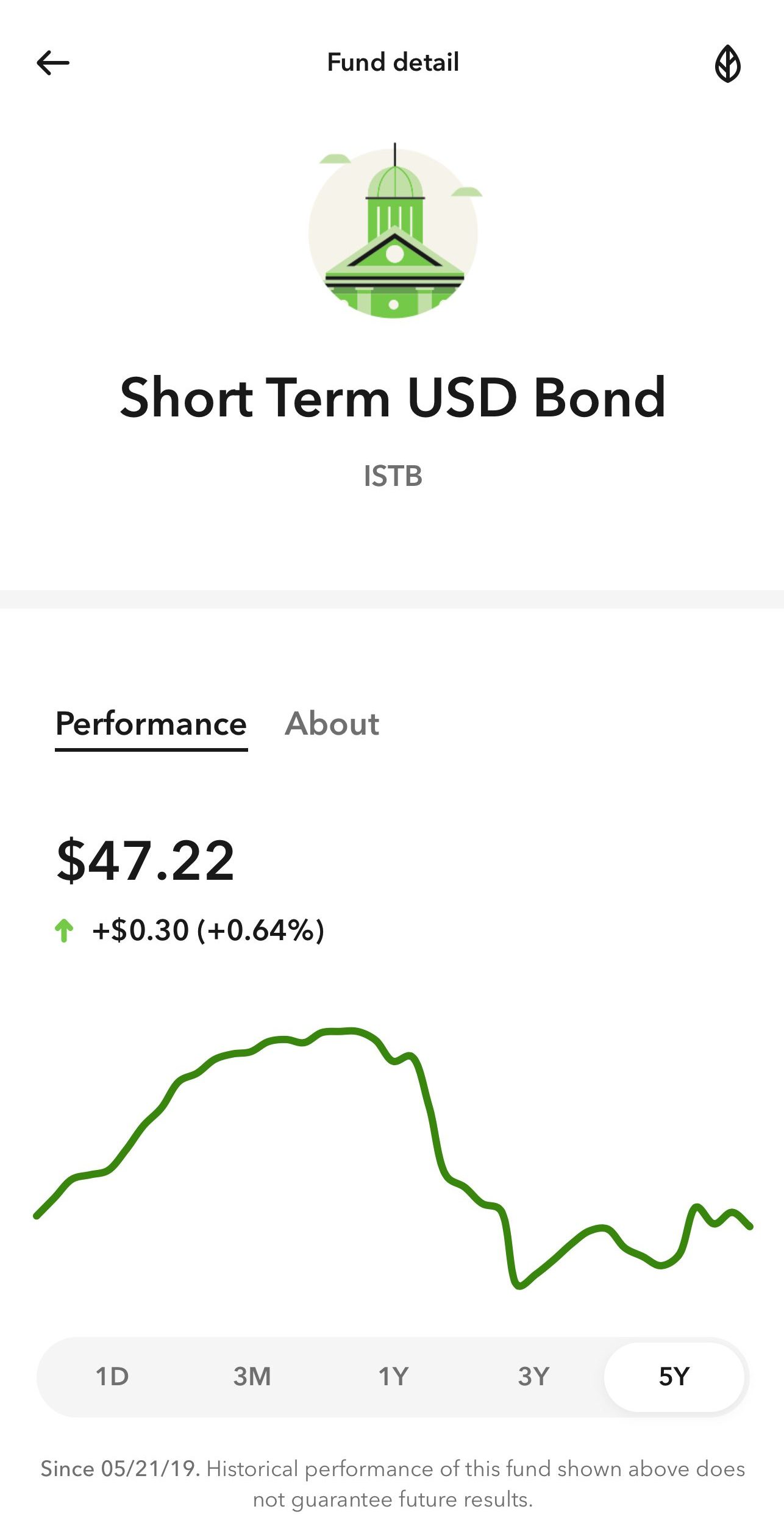
Many investing apps offer bond portfolios curated by experts.
With these, you can gain exposure to hundreds of different bonds within the same sector, risk level, and other parameters.
Here is an example of a short-term bond managed by Acorns.
3. Options To Invest In Bonds
Understanding the nuances of bond investing options is crucial for aligning your investment strategy with your financial goals, risk tolerance, and desired level of involvement in managing your portfolio:
-
Individual Bonds
Individual bonds offer precise control over your investment, allowing you to select specific issuers, credit qualities, and maturities. This specificity enables tailored risk management and predictable income streams, as you receive fixed interest payments until maturity.
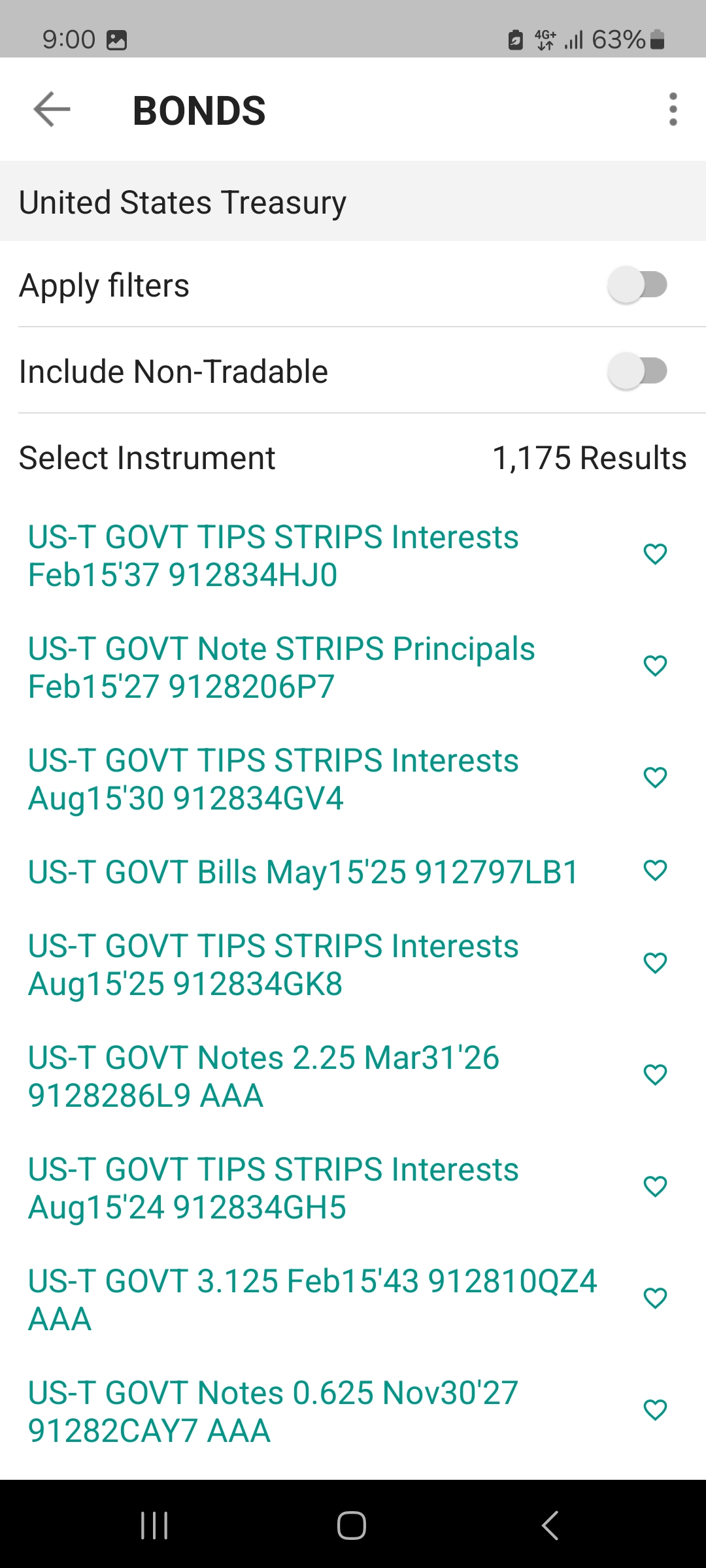
However, compared to bond ETFs and funds, individual bonds require a larger capital outlay for diversification and can be less liquid.
They're more suited for investors seeking stability and predictability who are willing to manage their portfolios actively.
-
Bond ETFs
Bond ETFs provide a blend of diversification and liquidity not typically available with individual bonds. They offer real-time trading and price transparency, similar to stocks, allowing for flexibility in response to market changes.
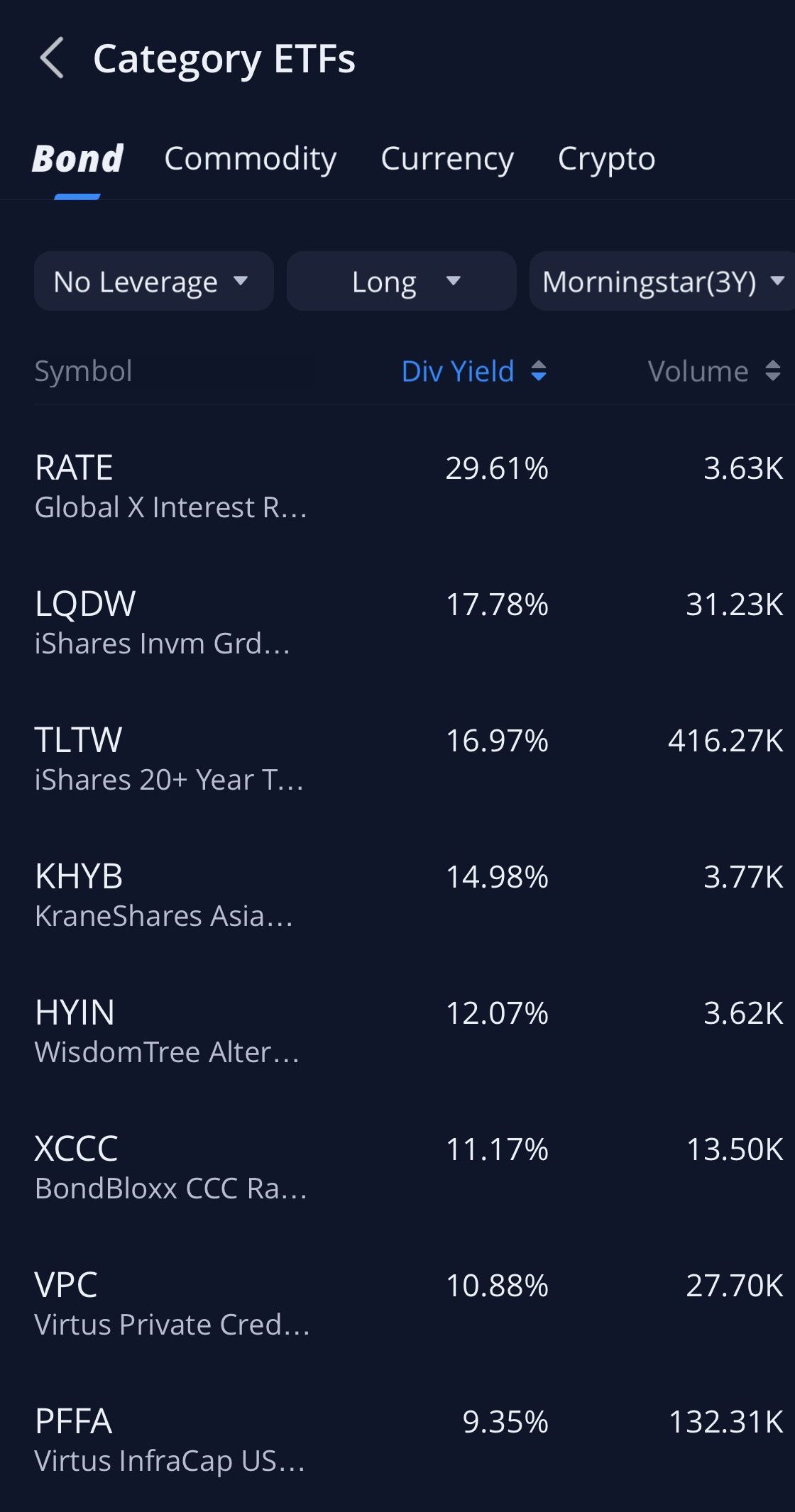
While they offer easier diversification than individual bonds, ETFs can experience price volatility and may not guarantee fixed income or return of principal.
They're ideal for investors seeking market-like returns with bond-level risk, without the need to manage numerous individual securities.
-
Bond Funds
Bond funds offer professional management and diversification across many bonds, reducing the impact of any single bond's performance on your investment.
Unlike individual bonds, they don't have a set maturity date, and their value fluctuates daily. This can introduce more uncertainty regarding returns compared to individual bonds but offers greater diversification than buying bonds individually.
However, they come with management fees, which can erode returns over time, a factor less concerning with individual bonds or ETFs.
Bond funds are suitable for investors who prefer a hands-off approach but still want exposure to the bond market.
4. Pick Bonds That Align With Your Goals & Strategy
Picking bonds that align with your investment goals and strategy requires a thoughtful approach, considering various factors that match your financial objectives and risk tolerance. Here's how you can do it:
Define Your Investment Goals: Identify what you're aiming to achieve with your bond investments. Are you looking for regular income, capital preservation, or perhaps a mix of both? Your goals will significantly influence the type of bonds you should consider.
Assess Your Risk Tolerance: Understand your comfort level with risk. Government bonds are typically lower risk compared to corporate or high-yield bonds. If you're risk-averse, you might lean towards treasuries or highly-rated municipal bonds. Conversely, if you're willing to accept higher risk for potentially greater returns, corporate or high-yield bonds might be more suitable.
Consider Maturity Profiles: Align the bond's maturity with your investment horizon. If you need access to your capital at a specific time, choose bonds that mature around that period. Shorter-term bonds are less sensitive to interest rate changes, while longer-term bonds typically offer higher yields but come with increased interest rate risk.
Evaluate Credit Quality: Bonds are rated based on their creditworthiness. Higher-rated bonds (AAA to BBB-) are considered investment grade and are less likely to default. Lower-rated bonds (BB+ and below) are high-yield or “junk” bonds, offering higher returns but with increased risk of default.
Diversify Your Bond Holdings: Don't put all your eggs in one basket. Diversification can help reduce risk. Consider diversifying across different types of bonds, issuers, and maturities to spread out potential risks.
Interest Rate Environment: Understand the current interest rate environment. When interest rates rise, bond prices typically fall, and vice versa. If you anticipate interest rate changes, choose bonds or bond funds that align with your outlook.
Tax Considerations: Be aware of the tax implications of your bond investments. For example, municipal bonds may offer tax-free interest income, which can be advantageous if you're in a higher tax bracket.
By carefully considering these factors, you can select bonds that not only align with your financial goals and risk tolerance but also contribute to a well-rounded and strategic investment portfolio.
5. Monitor and Rebalance
Monitoring and rebalancing your bond investments are critical steps to ensure your portfolio remains aligned with your financial goals and risk tolerance.
Here's a structured approach to effectively monitor and rebalance your bond holdings:
Set Review Intervals: Establish a regular schedule to review your bond investments. This could be quarterly, semi-annually, or annually. Consistent monitoring helps you stay informed about your portfolio's performance and the broader market conditions.
Assess Performance: Evaluate the performance of your bond investments relative to their benchmarks and your investment objectives. Look at factors such as yield, interest payments, and any capital appreciation or depreciation.
Check Credit Ratings: Regularly review the credit ratings of the bonds or issuers in your portfolio. Downgrades can affect bond prices and your portfolio's risk profile.
Interest Rate Environment: Stay informed about the interest rate environment as it has a significant impact on bond prices. Rising rates generally lead to falling bond prices and vice versa.
Duration and Maturity: Assess the duration and maturity profile of your bond portfolio. Ensure it aligns with your investment horizon and interest rate outlook. Adjusting the duration can help manage interest rate risk.
Diversification: Evaluate the diversification of your bond portfolio across different types, sectors, geographies, and issuers. Diversification can help mitigate risk.
Rebalancing: If your review reveals deviations from your target asset allocation or risk profile, rebalance your portfolio. This may involve buying or selling bonds or bond funds to realign your portfolio with your strategic asset allocation.
Tax Considerations: Be mindful of the tax implications of buying and selling bonds, especially in taxable accounts. Consider tax-exempt bonds or tax-efficient strategies if appropriate.
Professional Advice: If you're unsure about your ability to monitor and rebalance effectively, consider seeking advice from a financial advisor. They can provide expertise and guidance tailored to your investment goals.
By systematically monitoring and rebalancing your bond portfolio, you can adapt to changing market conditions, maintain a risk level you're comfortable with, and stay on track to achieve your investment objectives.
FAQs
Bonds are generally considered safer than stocks, but their risk level varies depending on the issuer's creditworthiness and the bond's duration and type.
The coupon rate is the interest rate the issuer agrees to pay annually, while the yield reflects the actual return based on the bond's current price.
Assessing a bond's risk involves examining the issuer's credit rating, the bond's duration, and the interest rate environment.
Yes, bonds can be sold on the secondary market before maturity, but the price received may be more or less than the original purchase price.
A bond ladder is an investment strategy where bonds with different maturities are purchased to manage interest rate risk and provide regular income.
Inflation can erode the purchasing power of a bond's fixed interest payments, making them less valuable over time.
Bond prices inversely relate to interest rates; when rates rise, bond prices usually fall, and vice versa.

